


Contact: Manager Yang
Hotline: 950-4048-3964 (free)
Tel: 0510-85386636
Mobile: 18011518665
Shangmeng Technology Wuxi Co., Ltd.
Address: A1-602, Tianan Smart City, No. 228 Linghu Avenue, Xinwu District, Wuxi City, Jiangsu Province
National disinfection product specification definition and health safety evaluation requirements
Anti-microbial : The process of killing or inhibiting the growth and reproduction of bacteria by chemical or physical means . Including sterilization, bacteriostatic.
An antimicrobial is an agent that kills microorganisms or stops their growth. Antimicrobial medicines can be grouped according to the microorganisms they act against against. For example, antibiotics are used against bacteria and antifungals are used against fungi . They can also be classified according to their Agents that kill microbes are called microbicidal , while those that directly inhibit their growth are called biostatic . The use of antimicrobial medicines to treat infection is known as antimicrobial chemotherapy , while the use of antimicrobial medicines to prevent infection is known as antimicrobial prophylaxis .
The main classes of antimicrobial agents are disinfectants ("nonselective antimicrobials" such bleach ), which kill a wide range of microbes on non-living surfaces to prevent the spread of illness, antiseptics (which are applied to living tissue and help reduce infection during The term "antibiotic" is described as only those formulations derived from living microorganisms but is now also applied to synthetic antimicrobials, such as the sulphonamides , or fluoroquinolones . The term also used To be restricted to antibacterials (and is often used as a synonym for them by medical professionals and in medical literature), but its context has broadened to include all antimicrobials. Antibacterial agents can be further subdivided into bactericidal agents, which kill bacteria, and bacteriostatic Agents , which slow down or stall bacterial growth. In response, further advancements in antimicrobial technologies Have resulted in solutions that can go beyond simply inhibiting microbial growth. Instead, certain types of porous media have been developed to kill microbes on contact.
Bacteriostasis : The process of inhibiting or inhibiting the growth and reproduction of bacteria by chemical or physical means .
★ The “Regulations on Sanitary Safety Evaluation of Disinfection Products” implemented by the State on January 1 , 2010 clearly stipulates various inspection items and requirements for antibacterial and bacteriostatic agents.
Anti-bacterial preparation test items and requirements
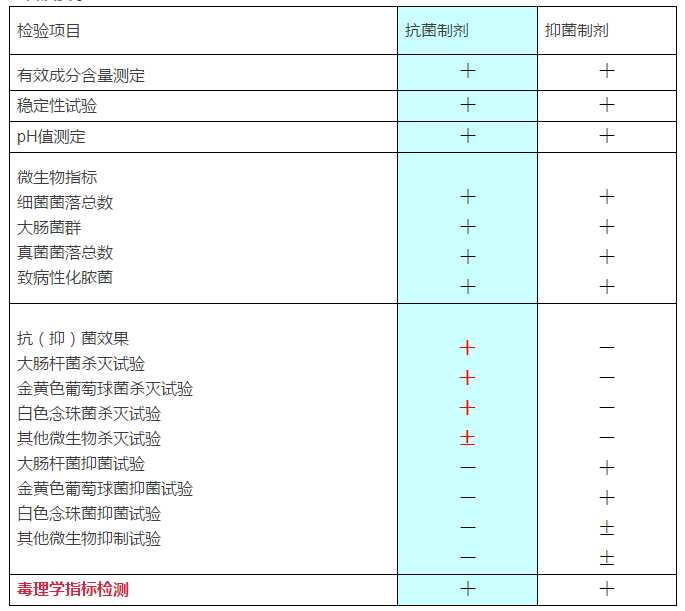
Note: “+” is a must-do project; “-” is not a project; “±” is an optional project. 1 is limited to chemical components. 2 The test is indicated in the instructions for use in products that have an effect on fungi or are used in the genital area. 3 The test instructions shall be carried out if the instructions for use have a killing or inhibiting effect on a particular microorganism. 4 In the instructions, the anti-bacterial preparation for skin should be tested for multiple skin irritation; the anti-bacterial preparations for mucosa indicated in the instructions should be used for eye irritation test for vaginal mucosal resistance ( The bacterial preparation should also be tested for vaginal mucosal irritation.
It can be clearly seen from the above table that the antibacterial agent is a killing effect and the bacteriostatic agent is an inhibitory effect.
The origin of antibacterial materials has been used since ancient times, and it is possible to keep certain microorganisms (bacteria, fungi, yeasts, algae, viruses, etc.) growing or reproducing at a level below the necessary level for a certain period of time.
Bactericides and bacteriostatic agents work in different ways. Bacteriostatic agents work by inhibiting bacterial growth (such as sulfonamides and macrolides); fungicides destroy bacterial cell structures and cause bacterial death (such as beta lactams). ).
In fact, there is no absolute limit to sterilization or inhibition. Some bacteriostatic agents also have a bactericidal effect when the concentration is high.
The distinction between fungicides and bacteriostatic agents appears to be carried out by experimentation. A simple experiment, such as the paper method, removes the drug-containing paper after 24 hours of culture, and continues to culture. If the bacteria in the inhibition zone re-grow, it shows a bacteriostatic agent. If it is not re-grown, it is displayed as a fungicide. .
Previous: China's photovoltaic glass scale is the world's first self-cleaning trend
下一条: Nanotechnology science to bring you 50 milestones in the history of nanotechnology
Address:Tianan Smart City A1-602, No. 228 Linghu Avenue, Xinwu District, Wuxi, Jiangsu, China TelePhone:0510-85386636 Fax:0510-85384339 E-mail:info@solmontech.com
KeyWord: