

Contact: Manager Yang
Hotline: 950-4048-3964 (free)
Tel: 0510-85386636
Mobile: 18011518665
Shangmeng Technology Wuxi Co., Ltd.
Address: A1-602, Tianan Smart City, No. 228 Linghu Avenue, Xinwu District, Wuxi City, Jiangsu Province

For the first time, researchers have produced highly porous, mechanically flexible and stretchable inorganic nanomaterials that are hydrophilic and hydrophobic. The material consists of interpenetrating hollow gallium nitride tetrapod, which has similar properties to biological cell membranes and can be used in applications such as sensors, microfluidic devices and micro-robots.
The biological cell membrane is composed of phospholipid structural units that attract and repel water. Phospholipids are hydrophilic due to their polar phosphate group "head" and are hydrophobic due to their inclusion of the non-polar "tails" of fatty acid chains.
By leading the research group Ion Tiginyanu at the Technical University of Moldova and Lai Adelung 's Keele University in Germany have now achieved such a dual hydrophobic-hydrophilic behavior of the first inorganic nanostructure. Researchers use materials such as gallium nitride (GaN), which is the second most important semiconductor after silicon. They used epitaxial deposition techniques, called hydride hydride vapor phase epitaxy, to produce GaN hollow microquarius on a four-legged microstructural template of zinc oxide (ZnO). These are called aerotetrapods or aerogalnite (aero-GaN) and are both hydrophobic and hydrophilic.
“We found that our structured GaN structure contains a mixture of micron and nanoscale features,” explains Tiginyanu. "Individual GaN aerotetrapod actually looks very much like an artificial pond skater, when placed on the water and interacts with water in a similar manner - that is, its downwardly positioned arm keeps four feet floating on the surface. ”
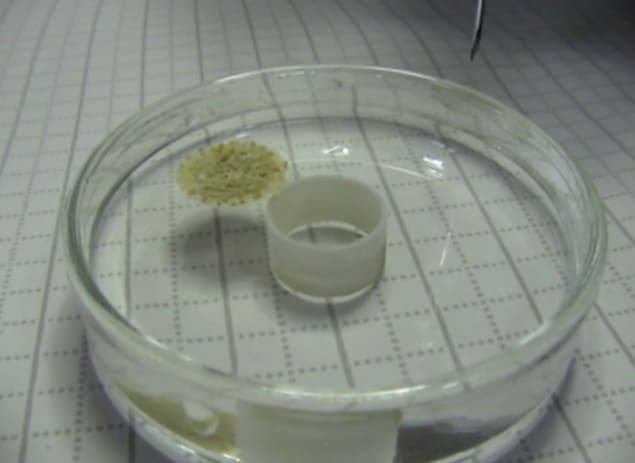
Researchers say they weave a waterproof raft from their materials by combining a large number of these four-legged animals. “Another animal analogy is very useful here,” says Tiginynau. “Because the pods interact with other animals in the same way that fire ants grip each other during the flood.” In fact, the scorpion can carry more than itself. Hundreds of droplets. It has a durable structure due to the electrostatic interaction between the nanometer thick walls of adjacent quadrupeds in the network.
"In the braided tweezers, the arms of the hollow quadruped are deformed, resulting in electrode polarization due to piezoelectric and flexural electrical phenomena," he explained.
He added that this is not all: aviation GaN can also be self-healing. “When we add more than a threshold amount of liquid, the aero-GaN筏 texture creates a hole that allows some of the liquid to leak. Once the load is exceeded, the raft seems to heal itself.”
The researchers also found that when they roll water onto a GaN quadruple bed, they can produce liquid marble GaN that covers the entire surface of the droplet. When GaN marble manufactured using an aqueous ethanol solution was placed in a petri dish containing water, it was advanced on the water surface at a speed of up to 750 rpm.
Tiginynau explained that the dual behavior comes from the hydrophilicity of the free end of the air quadruped arm, its closed plane coincides with the polar crystal c plane of GaN, and the hydrophobicity of the outer air-GaN wall. "This hydrophilic hydrophobic character of aero-GaN allows it to pass over the surface like a flying water lily beetle. It passes through four hydrophilic claws on the surface of the water, and the rest of the body is hydrophobic, so it is surfaced. Fight back," he told the physical world .
He added that our work has greatly expanded GaN's traditional applications in solid-state lighting and high-frequency/high-power microelectronics and nanoelectronics. Energy-efficient self-propelled MEMS structures, sensors, microfluidics and micro-robots are just some of the areas that may benefit.
“For example, aero-GaN-based energy-saving self-propelled liquid marbles can be used to control chemical reactions in confined spaces. Aero-GaN coated droplets can be used to make bioreactors for culturing cells, especially considering GaN. High chemical stability and biocompatibility.
Nano Energy 10.1016 / j.nanoen.2018.11.049 reports full details of the study .
Source: physorg website
Previous: New anti-fogging agents: nanotechnology and sunlight clear the barriers for better visibility
下一条: Bismuth catalysts create new efficiency records for water decomposition
Address:Tianan Smart City A1-602, No. 228 Linghu Avenue, Xinwu District, Wuxi, Jiangsu, China TelePhone:0510-85386636 Fax:0510-85384339 E-mail:info@solmontech.com
KeyWord: